|
|
|
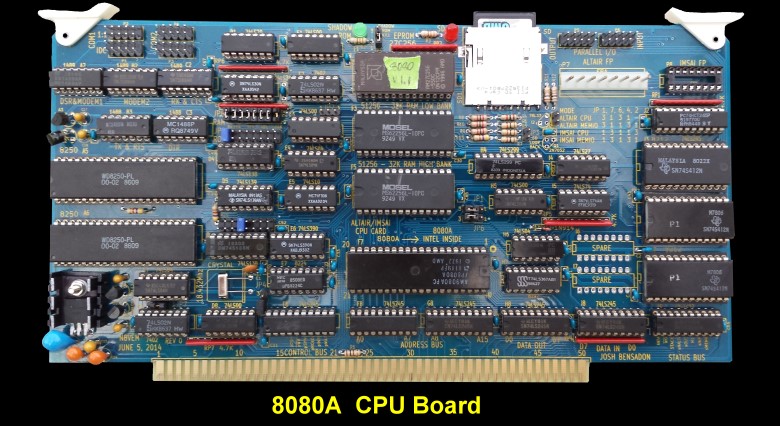
An S-100 8080 CPU Board.
|
|
|
Introduction
Every serious S-100 board manufacture had their own CPU card. Many had a number of them. While almost everybody started off with Altair or IMSAI cards. These early 8080 based cards were quickly replaced by faster Z80 CPU boards. Nevertheless most S100 and CPM based software stuck with the Intel 8080A, its software, and indeed the Intel based assembly nemonics.
If you look at the layout of the original MITS Altair 8080 CPU board you will notice that there are very few plated through holes on the board. That is because the (unknown) engineer who laid out the board picked the S100 pins that presented the shortest route to the CPU and the other components on the board. In contrast to, for example the Intel multibus, the S100 bus address, data and control lines have no order on the bus. This has allowed for the production of 8080 CPU boards with plenty of space to add extra components. Over the years some manufactures went on to produced 8080 CPU S100 boards with numerous "extra" components.
Recently Josh Bensadon of
The history of Intel's 8080 CPU can be seen here.
The 8080 CPU Board Circuitry
Before working with this board the manual (see below), should be read cover to cover.
The board can be configured as a bus master where the 8080A controls the bus completely or it can be configured in "slave mode" where the 8080A CPU is inactive but the other components on the board are active and available to another CPU on the bus. Note this "slave mode" should not be confused with the normal IEEE-696 definition of the S100 bus in slave mode where two bus CPU's transfer bus control back and forth between each other with a well defined handshake protocol (often one being a 16 bit CPU). Slave mode here essentially means a board with the UARTs, the SD card, 8212's etc being available to another CPU on the bus.
The board also has two connections that hook up correctly to either the Altair or IMSAI front panels. This conveniently allows you to review the CPU's in action, single step etc.
Address lines.
Pushing the sixteen 8080 address lines out on to the S-100 bus on this 8080 board is not complicated. The two 74LS245 bus drivers (IC-G8 and IC-F8) , do the job. Pin 1 of each chip is grounded so the direction is always away from the CPU. As for most S100 CPU boards the address lines can be disabled by lowering the ADDR DSBL S100 pin #22. This for example would be done by a DMA controller on the bus.
Data lines.
The S100 bus in 8 bit mode utilizes a separate data in and data out bus. On this board it is handles by two 74LS245 bus drivers (IC-I8 and IC-H8). The direction (pin 1 in each case) is determined by the jumpers JP4 & JP5. In the normal master mode they are jumpered 2-3 in each case. Directions is normally from the CPU (I8 and H8, pin 1 high) except for CPU reads/data in, where the DBIN signal to gate D1 lowers pin 1 of I8.
Status lines.
The 8080A status lines essentially need no modifications and are posted directly to the S100 bus via IC-J7 and IC-J8.
Control lines.
Likewise the 8080A control lines need no modifications and are posted directly to the S100 bus via IC-E8.
The 8080A was the last of it's kind to require multiple input voltages. It required a 12V, -5V and 5V input. It also required an elaborate clock structure, reset and ready signal. These are provided by E7, an Intel 8224 clock generator. With the onboard UARTs (see below), the board has no less than 6 different voltage regulators! The primary 5V regulator (A7) supplies most of the power to the board. It should be a 7805C 1.5 Amp regulator. Because the heat sink area is quite small special care must be used to get as much heat radiated away from the board as possible. Use heat sink compound, a mica washer between the board and heat sink if possible. I actually have one small heat sink inside the other to have more heat radiation fins.
UARTS
The board has two 8250 UARTS (IC-A5 & IC-A6) along with RS232 line drivers 1488's and 1489's. The RS232 signals are brought up to the top of the board and can be connected via the headers P1 and P2.
PARALLEL PORTS
The board also has an a bit parallel port. Actually two (IC-J3 and IC-J5), one for input, one for output. These are implemented with standard 8212's. For more information is programming and using these chips see our Parallel Ports board.
SD Card
One really neat aspect of this card is the presence of an SD card socket. This will allow the 8080 card to directly execute any HEX file stored on the SD memory card. A BIOS is
8080 CPU Board Releases
There are now two versions of this board. They are slightly different. They can be seen here:-
Rev 0 – Released June 5, 2014 (This was the first version of the board).
Rev 1 – Released April 9, 2016 This board is still available. Contact CrustyOMO or post on the Google Groups S100Computers forum if you would like one.
Other Information related to these boards
IMASI RAM.pdf
IMSAI CLK.jpg
IMASI MPU.pdf
IMASI CPA 2014.pdf
Other pages describing S-100 hardware and software.
Please click here to continue...
This page was last modified on 02/05/2019